Understanding the Sugar Cravings Cause: Tips to Control Your Sweet Tooth

Why do we crave sugar? The causes are both physical and mental. Physically, low nutrients make us seek quick energy from sugar. Mentally, sugar releases serotonin and dopamine, making us feel good and want more. This article explores the sugar cravings cause and offers tips to control them.
Key Takeaways
-
Understanding sugar cravings involves recognising both physiological responses and emotional triggers, allowing for better meal and lifestyle choices.
-
Maintaining stable blood sugar through balanced meals with proteins, healthy fats, and fibre is key to reducing sugar cravings.
-
Adequate sleep, regular exercise, and mindful eating can support efforts to manage sugar cravings naturally—empowering you to take charge of your health.
Why Do We Crave Sugar?

Imagine a day where you haven’t had enough to eat, and by evening, you’re reaching for sugary snacks. Why does this happen? The body often seeks quick sources of energy like sugar when it hasn’t received enough nutrients throughout the day. This is a physiological response designed to keep us going, but it can lead to excessive sugar consumption if not managed properly, especially when considering afternoon snack intake, eating enough, and unintentional weight gain.
But it’s not just about energy. Sugar activates consumption triggers the release of brain chemicals such as serotonin and dopamine, which create feelings of pleasure. This can make sugary foods incredibly hard to resist, especially when there is much sugar involved. No wonder sugar cravings can feel like a sugar addiction; they are fuelled by both physiological and psychological factors.
Understanding these underlying reasons can help you develop strategies to manage your cravings. Whether it’s ensuring you get enough nutrients throughout the day or finding healthier ways to boost your mood, tackling these triggers head-on is key to curbing your sugar habit.
The Role of Blood Sugar Levels
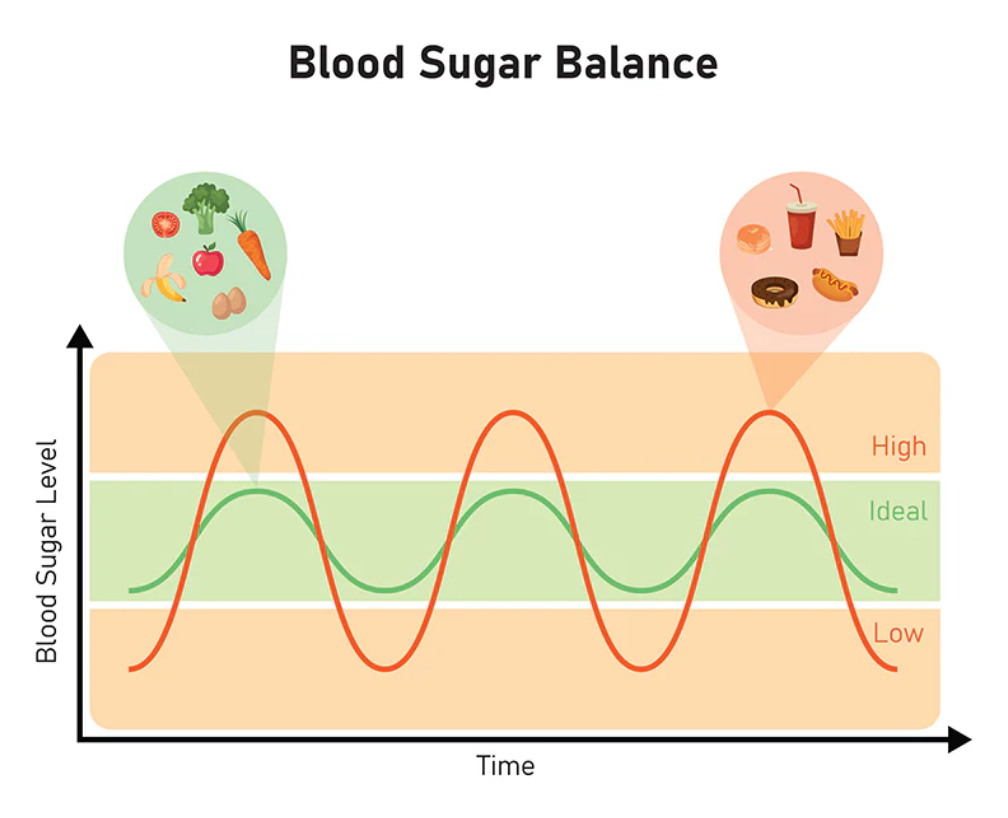
Blood sugar levels play a significant role in sugar cravings. When you consume simple carbohydrates and complex carbs, your blood sugar levels spike rapidly, only to crash soon after. This roller-coaster effect makes you crave more table sugar to bring your energy levels back up. Starchy foods and even 'natural sugars' like honey and brown sugar can cause similar surges and crashes.
Maintaining stable blood sugar levels requires including protein, fat, and fibre in your meals. These nutrients digest more slowly, preventing the rapid spikes and crashes that trigger cravings. Protein, in particular, is a game-changer. It digests slowly and keeps you full for longer, reducing the likelihood of a blood sugar spike that leads to cravings. Fibre also plays a vital role in fighting cravings by keeping you full and preventing blood sugar crashes.
Emotional Triggers for Sugar Cravings
Emotional eating is a common culprit behind sugar cravings. Stress from work, financial issues, or personal relationships can lead us to seek comfort in high-calorie, sweet foods. It’s a coping mechanism that provides temporary relief but can have long-term consequences on our health.
Keeping a food diary can be a powerful tool in recognising the link between your emotions and eating behaviours. Identifying patterns allows you to address the root causes of your cravings. Physical activity can also positively influence your mood and help manage the urge to consume high-calorie snacks, contributing to better mental health. Even short bouts of exercise can serve as an effective strategy to decrease cravings, especially during stressful situations.
Engaging in activities like walking, watching a movie, or even chewing gum can serve as healthy distractions from cravings driven by boredom or stress. Finding healthier ways to cope with emotions reduces your reliance on sugary foods for comfort.
The Impact of Sleep on Sugar Cravings

Sleep deprivation is a significant factor in sugar cravings. When you’re sleep-deprived, hunger hormones like ghrelin increase, while leptin, the hormone that signals fullness, decreases. This imbalance makes you more likely to crave sugary foods as your body seeks quick sources to eat sugar for energy.
To manage sugar cravings effectively, aim for seven to nine hours of sleep each night. Adequate sleep helps regulate how your brain processes food, reducing the likelihood of how much sugar craving sugar. Prioritising good sleep hygiene is crucial for controlling your sugar cravings.
How Artificial Sweeteners Influence Cravings

Artificial sweeteners might seem like a good alternative to sugar, but they can actually increase cravings for sugary foods. Consuming these sweeteners can lead to an increased appetite for sweeter foods and alter your taste preferences, making you crave more sweetness over time.
Moreover, artificial sweeteners can disrupt the gut microbiome, potentially affecting metabolic health. This disruption can lead to increased cravings and other health issues. Understanding the impact of artificial sweeteners enables you to make more informed choices and manage your sugar cravings better.
How to Stop Sugar Cravings Naturally
Stopping sugar cravings naturally starts with mindful choices in both diet and lifestyle. Simple strategies, like eating balanced meals, avoiding late-night eating, and following the right food order, can help prevent, manage, and reduce sugar cravings effectively. With consistency, these small changes can make a big impact on your overall health and energy.
Eat Balanced Meals
Eating balanced meals is crucial for stabilising blood sugar levels and managing sugar cravings. Incorporating high-quality proteins, healthy fats and complex carbohydrates into your diet can help keep your blood sugar balanced and reduce the likelihood of experiencing intense cravings. Aim for 30g of protein per meal to enhance satiety and stabilise your blood sugar levels. Protein digests slowly, keeping you full for longer and preventing sudden spikes and crashes in blood sugar, which are known to trigger cravings for sugary foods. By prioritising protein, you can effectively manage your sugar cravings and maintain a healthy weight.
When you focus on balanced meals, the chances of craving sugary foods decrease significantly. Ensuring that each meal is well-rounded effectively curbs your sugar cravings and helps you lose weight while maintaining a healthy weight.
Stop Eating 2 - 3 Hours Before Bedtime
Avoiding food 2 to 3 hours before bedtime can play a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and supporting metabolic health. When you eat close to bedtime, your body must continue digesting while it’s supposed to be winding down, which can lead to elevated nighttime glucose and insulin levels. This can interfere with sleep quality and increase the likelihood of morning cravings, especially for sugar and refined carbs.
By stopping food intake several hours before sleep, you give your body time to stabilise blood glucose and enter a natural fasting state. This aligns with the principles of intermittent fasting, which involves alternating periods of eating and fasting to support insulin sensitivity, fat metabolism, and appetite regulation. Extending your overnight fasting window not only allows insulin levels to drop more efficiently but also enhances cellular repair processes, such as autophagy, that occur more effectively during a fasted state. Over time, this can contribute to better blood sugar control, reduced cravings, improved energy levels, and more stable moods. Incorporating this habit into your routine can make a significant difference, especially when combined with nutrient-dense meals earlier in the day that promote stable energy and satiety.
The Power of Eating in the Right Order: Fibre First, Carbs Last (If at All)
The order in which you eat your food can dramatically impact your blood sugar response—and by extension, your energy, cravings, and long-term metabolic health. Starting with fibre-rich vegetables or leafy greens is one of the most effective strategies to blunt post-meal glucose spikes. Fibre acts as a barrier in the digestive tract, slowing the absorption of sugars and starches that follow, which helps prevent sharp rises in blood glucose.
Next, focus on eating your protein and healthy fats. These macronutrients further slow digestion, promote satiety, and stabilise your insulin response, reducing the likelihood of a blood sugar crash that can lead to intense cravings—especially for sweet foods.
If you choose to eat carbohydrates, save them for last. By the time you reach them, the fibre, protein, and fat you've already consumed have created a buffering effect that significantly reduces the glycaemic impact of the carbs. This simple shift in meal sequence can help you avoid the rapid blood sugar spikes and crashes that drive hunger and sugar addiction.
Importantly, carbohydrates are not an essential macronutrient. Unlike protein and fat—which the body needs for critical functions like muscle repair, hormone production, and cell structure—there is no biological requirement for dietary carbohydrates. Your body is fully capable of producing the small amount of glucose it needs via gluconeogenesis, a process that converts protein or fat into glucose.
By being intentional about the order in which you eat and recognising that carbs are optional, not essential you can take powerful control over your metabolic health, reduce cravings, and support long-term weight and energy balance.
The Benefits of High-Protein Breakfasts

Starting your day with a high protein meal can enhance feelings of fullness and help regulate your appetite throughout the day. A protein-rich meal in the morning can suppress the hunger hormone ghrelin and elevate hormones that signal fullness.
Eating eggs or other protein sources during breakfast can make you less likely to crave sweet foods later in the day. High-protein breakfasts are also linked to lower glucose responses, which can help mitigate sugar cravings.
The Role of Gut Health in Managing Sugar Cravings
A balanced gut microbiome can help regulate cravings for sugar, potentially reducing their intensity. Consuming fermented foods can support a diverse gut microbiome, which is linked to improved regulation of sweet cravings.
Incorporating fermented foods into your diet introduces beneficial bacteria that can alter the gut microbiome, leading to healthier food cravings. Focusing on gut health is a significant step towards managing your sugar cravings more effectively.
Exercise as a Tool to Curb Cravings

Engaging in moderate exercise can serve as a distraction from cravings for sugary snacks. Exercise reduces stress hormones, which can lessen the urge to indulge in sugary foods. Brisk walking, in particular, is an effective mode of exercise that helps reduce the urge for sugary snacks.
Overall, physical activity encourages healthy foods while helping to manage cravings. Incorporating a healthy diet and regular exercise into your routine helps you better control your sugar cravings and improve your overall health benefits.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you feel overwhelmed by sugar cravings, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider. Persistent sugar cravings can be linked to hormonal imbalances, gut infections, or adrenal fatigue, which require professional attention. Consuming too much sugar may also contribute to these issues.
Functional medicine doctors can help identify underlying issues related to sugar cravings and may prescribe medications to aid in reducing them. If your efforts to control sugar cravings fail despite trying various strategies, seeking a mental health professional is advisable.
The Role of Berberine in Reducing Sugar Cravings
Berberine, a natural compound found in several plants, has gained attention for its potential to help reduce sugar cravings. This powerful alkaloid is known for its ability to support metabolic health, making it a valuable addition to your strategy for managing sugar cravings.
Berberine works by influencing several biological pathways that regulate metabolism and blood sugar levels. It activates an enzyme called AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), often referred to as the "metabolic master switch." By activating AMPK, berberine helps improve insulin sensitivity and promotes the uptake of glucose into cells, reducing blood sugar levels.
Why Berberine Helps with Sugar Cravings
By stabilising blood sugar levels, berberine can help prevent the rapid spikes and crashes that often lead to intense sugar cravings. When your blood sugar is balanced, your body is less likely to seek out quick sources of energy like sugary foods. Additionally, berberine's ability to enhance insulin sensitivity can further reduce cravings by ensuring a more stable energy supply throughout the day.
Incorporating Berberine into Your Routine
To leverage the benefits of berberine for sugar cravings, consider incorporating it as a supplement in your daily routine. However, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
By adding berberine to your regimen, you can support your body's natural ability to maintain balanced blood sugar levels, making it easier to manage and ultimately reduce your sugar cravings. This, combined with a healthy diet, regular exercise, and mindful eating, can empower you to take control of your sugar habit and enhance your overall well-being.
Summary
In summary, understanding the reasons behind sugar cravings and the factors that influence them is crucial for managing your sweet tooth effectively. From physiological and psychological triggers to the impact of blood sugar levels, sleep, and gut health, multiple factors play a role in sugar cravings.
Adopting simple, sustainable strategies—like eating balanced meals, avoiding food close to bedtime, following the right food order and staying active—can make a powerful difference. If your cravings ever feel overwhelming, don’t hesitate to seek support from a health professional. With these tools and insights, you’re already on the path to gaining control over sugar cravings and embracing a healthier, more energised life.
Researched and reviewed by Dr Elena Seranova, Ph.D.
Dr Seranova holds a master's degree in Translational Neuroscience from the University of Sheffield, UK, and a Ph.D in Stem Cell Biology and Autophagy from the University of Birmingham, UK. She is a published author in multiple peer-reviewed journals, including Cell Reports and Developmental Cell.
LEARN MORE!






Leave a comment