At What Age Does NAD+ Decline and How It Impacts Your Health

NAD+ levels, essential for various cellular functions, begin to decline around age 30, raising the question of what age does NAD+ decline. This decline accelerates as we age, impacting overall health. In this article, we’ll explore how NAD+ levels change with age and the implications for your well-being.
Key Takeaways
-
NAD+ levels start to decline after age 30, contributing to cellular damage and age-related health issues.
-
Factors influencing NAD+ decline include increased activity of NAD+ consuming enzymes, obesity, genetic predispositions, and lifestyle choices.
-
NAD+ deficiency can lead to symptoms like fatigue, cognitive decline, and skin changes, emphasising the importance of maintaining optimal NAD+ levels for overall health.
Understanding NAD+ and Its Importance

NAD+, also known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, is a coenzyme. It is present in every cell of the body. This coenzyme is involved in numerous cellular functions, such as energy metabolism, DNA repair, and managing cellular stress. Essentially, NAD+ acts as a helper molecule, facilitating critical biochemical reactions that keep our cells healthy and functioning optimally.
One of the primary roles of NAD+ is in energy metabolism. It is crucial for converting nutrients from the food we eat into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell. Without adequate NAD+ levels, this conversion process is impaired, leading to reduced energy production and overall cell metabolic dysfunction.
In addition to energy production, NAD+ is vital for DNA repair mechanisms. Our DNA is constantly subjected to damage from various sources, including environmental toxins and oxidative stress. NAD+ is vital for activating enzymes involved in repairing this damage, ensuring the integrity of our genetic material and preventing mutations that could lead to diseases.
Balanced NAD+ levels are vital for normal cellular functions and overall cell survival. As a major player in regulating gene expression and responding to cellular stress, NAD+ helps cells adapt to changes and maintain homeostasis. Its critical role extends to influencing physiological function, making it an essential molecule for overall health.
Overall, NAD+ is indispensable for cellular health, energy metabolism, and DNA protection. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it underpins many of the processes that keep us healthy and vibrant. Next, we’ll explore how NAD+ levels change with age and the implications of this decline on health. Delving into the science behind NMN can provide insights into ways to potentially address these changes.
Age-Dependent Decline of NAD+ Levels
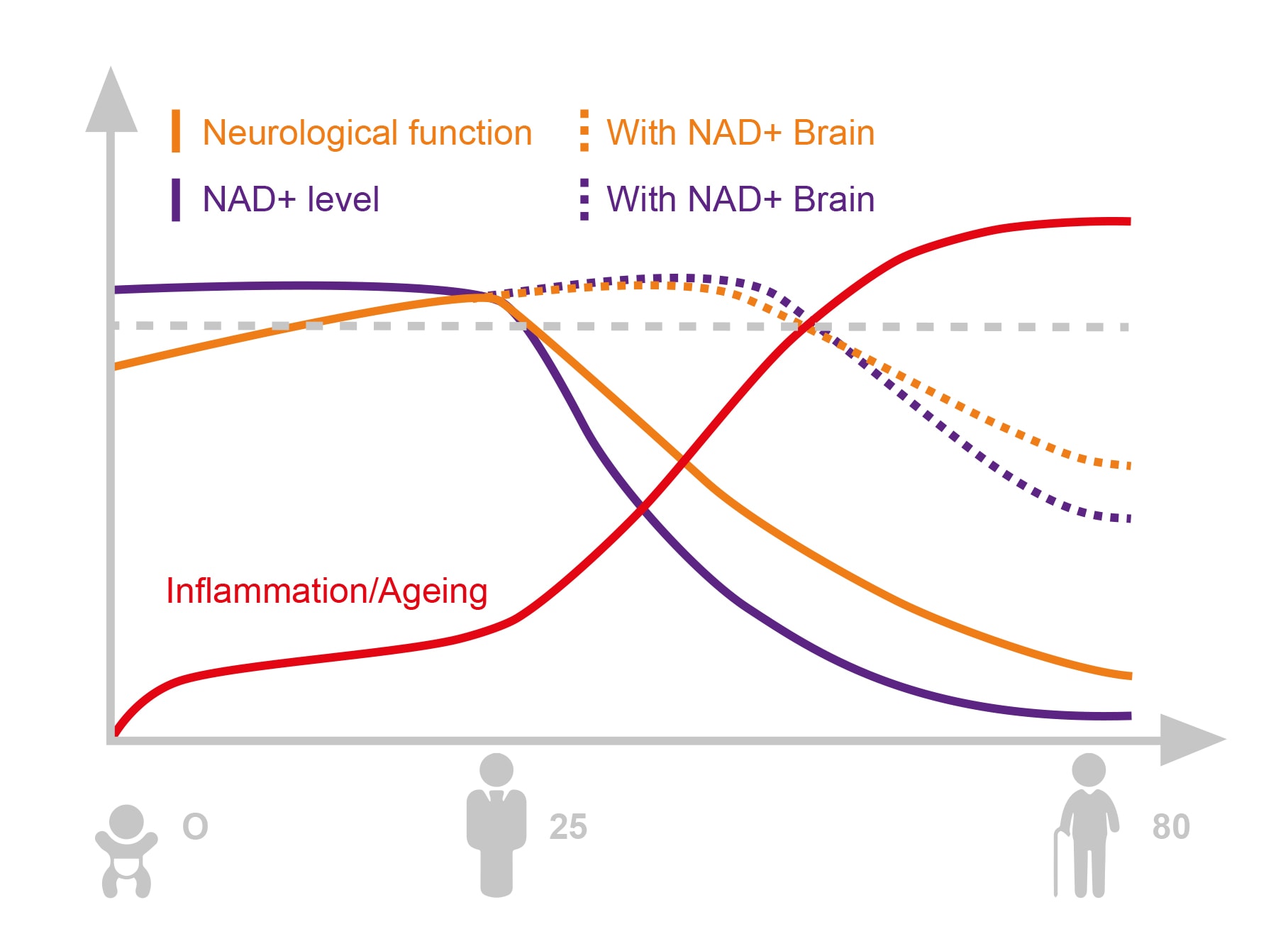
The decline of NAD+ levels as we age is a well-documented phenomenon. Research indicates that NAD+ levels typically start to decline after age 30, with significant decreases observed between young adults and middle age. This age-dependent decline is a critical factor in understanding the aging process and its associated health issues, including age related NAD+. Ages play a significant role in this context.
The decline in NAD+ is not uniform across all tissues and other tissues. Studies have shown that while some tissues may experience a significant drop in NAD+ levels, others may remain relatively stable. For instance, mitochondrial NAD+ levels might stay constant even when total tissue NAD+ levels are observed to decline. This variability highlights the complexity of NAD+ metabolism and its regulation across different cell types and organs.
The age-related decline in NAD+ levels actively contributes to cellular damage and age-related diseases. It actively contributes to cellular damage and exacerbates age-related diseases. As NAD+ levels drop, cells become less capable of repairing DNA damage and responding to stress, leading to an accumulation of cellular damage over time. This progressive decline is a hallmark of the aging process and is linked to various age-related conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic disorders.
Studies indicate that NAD+ levels in the brain decrease significantly with age, contributing to cognitive decline and brain aging. Similarly, lower NAD+ levels are associated with mitochondrial dysfunction, which is a major factor in the aging process and the development of age-related diseases.
The decline of NAD+ in human cells is a universal truth of aging, affecting everyone to varying degrees, including their other half. By the time individuals reach middle age, their NAD+ levels can be less than half of what they were in their youth. Understanding this decline helps develop strategies to mitigate its impact and improve health span, as discussed in trends cell biol.
Factors Influencing NAD+ Decline
Several factors contribute to the decline of NAD+ levels with age. A primary mechanism involves the increased activity of NAD+ consuming enzymes. These enzymes, such as poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) and sirtuins, play vital roles in DNA repair and stress responses but consume NAD+ in the process. As we age, the activity of these enzymes increases, leading to a greater depletion of NAD+.
Another significant factor is the activity of Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT), an enzyme whose activity increases with obesity and age. NNMT diverts NAD+ precursors away from NAD+ synthesis, further contributing to the decline in NAD+ levels. Excess nicotinamide can also be metabolised in alternative pathways, adversely affecting NAD+ levels.
Genetic predispositions significantly influence the regulation of NAD+ metabolism. Variations in genes encoding enzymes for NAD+ synthesis and consumption can impact the rate of NAD+ decline with age. This genetic variability means that some individuals may experience a more pronounced decline in NAD+ levels than others.
Diet and exercise are lifestyle choices that significantly impact NAD+ levels. A sedentary lifestyle and poor dietary habits can accelerate the decline of NAD+, while regular physical activity and a nutrient-rich diet can help maintain healthier levels. Hormonal changes, particularly in women, may also influence NAD+ levels and their redox state as they age.
Certain health conditions, such as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), can impact NAD+ metabolism, affecting the severity and treatment of the condition. Overall, the decline of NAD+ is influenced by a complex interplay of enzyme activity, genetic factors, lifestyle choices, and health conditions, making it a multifaceted issue that requires a holistic approach to manage.
Health Implications of Declining NAD+ Levels
The consequences of declining NAD+ levels are far-reaching and impact various aspects of health. Here are some significant changes in implications:
-
Impaired cellular response to stress
-
Increased DNA damage
-
Cells become less capable of repairing DNA damage
-
Accumulation of genetic mutations
-
Cellular dysfunction
These factors can contribute to various health issues as NAD+ levels continue to further decline.
This decline is closely linked to various metabolic and physiological dysfunctions associated with ageing. Chronic inflammation, a common feature of aging, increases the activity of NAD+ consuming enzymes, further depleting NAD+ levels. This creates a vicious cycle where declining NAD+ levels exacerbate inflammation and oxidative stress, accelerating the aging process and contributing to age-related disorders.
One of the critical areas affected by low NAD+ levels is mitochondrial function. Mitochondria, the powerhouses of the cell, rely on NAD+ for energy production. Lower NAD+ levels lead to mitochondrial dysfunction, which is a significant factor in age-related cognitive decline and other neurodegenerative diseases. Supporting NAD+ levels may offer therapeutic benefits in managing these conditions, highlighting the importance of maintaining healthy NAD+ levels for overall health.
Muscle weakness and reduced physical performance are also associated with low NAD+ levels. As NAD+ plays a vital role in energy metabolism, its decline can lead to decreased stamina and muscle function. Additionally, NAD+ deficiency can influence emotional states, leading to mood instability and increased anxiety. Maintaining adequate NAD+ levels as we age is essential for physical and mental health.
In summary, the age-dependent decline of NAD+ levels is a critical factor in the aging process and is associated with various health complications. By understanding these implications, we can better appreciate the importance of strategies aimed at boosting NAD+ levels to support overall health and well-being.
How to Test Your NAD+ Levels
Testing NAD+ levels is a practical step toward understanding cellular health and metabolism. One of the most convenient methods available today is an at-home NAD+ test kit. These kits allow individuals to accurately establish their baseline NAD+ levels before starting any supplementation or lifestyle changes aimed at boosting NAD+.
An at-home test usually involves a blood-spot assay card, enhancing the stability of NAD+ samples during transport for analysis. This method is user-friendly and provides reliable results, making it accessible for anyone interested in monitoring their NAD+ levels.
Once the samples are collected, they are analysed using high-resolution liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). This advanced technique ensures precise measurement of plasma NAD+ levels in the blood, providing valuable insights into a person’s cellular health. Testing total NAD+ levels can reveal imbalances that may be affecting your energy metabolism and overall well-being.
Regular testing allows you to track NAD+ levels over time and adjust lifestyle or supplementation strategies as needed. This proactive approach empowers you to take control of your health and potentially mitigate the effects of aging.
Strategies to Boost NAD+ Levels
Maintaining healthy NAD+ levels is vital, and several strategies can naturally boost NAD+ levels. Incorporating raw foods high in vitamin B into your diet is one effective approach. Foods such as avocados and steamed fish are rich in these essential nutrients and can help elevate NAD+ levels.
Fermented foods, like sauerkraut and kombucha, are also beneficial. These foods contain compounds that support NAD+ production and can be a tasty addition to your diet. Intermittent fasting may enhance the body’s NAD+ supply by triggering metabolic responses that boost levels.
Using saunas or hot tubs can stimulate NAD+ production. The increased energy demands placed on the body in high-heat environments can lead to higher NAD+ levels. Limiting sun exposure helps conserve NAD+ levels, as UV rays require more NAD+ for skin repair.
These lifestyle adjustments, combined with a balanced diet, can help maintain and even boost your NAD+ levels, supporting better health and helping you stay healthy for longevity.
Common Symptoms of NAD+ Deficiency
NAD+ deficiency can manifest in various symptoms, affecting both physical and mental health. Common signs are:
-
Fatigue
-
Cognitive decline
-
Poor sleep quality
-
Skin changes
Individuals with low NAD+ levels often experience feelings of sluggishness and fatigue, making it challenging to perform daily activities.
Mental fog, difficulty focusing, and memory issues also indicate NAD+ deficiency. These cognitive impairments can significantly impact quality of life, making it crucial to address NAD+ levels if such symptoms are present. Learn more about mental fog and how it relates to ADHD and quality of life at NMN Bio.
Additionally, disruptions in sleep patterns and overall sleep quality can be linked to low NAD+ levels. Skin vitality may diminish, leading to increased dryness and the development of wrinkles. Early recognition of these symptoms can prompt timely interventions to restore NAD+ levels and improve health.
Severe NAD+ Deficiency and Major Risk Factors
Severe NAD+ deficiency results in pronounced symptoms and significant health risks. Cognitive issues such as memory loss and confusion are common, along with physical symptoms similar to pellagra, including dermatitis and diarrhea. These severe symptoms highlight the importance of maintaining adequate NAD+ levels.
Obesity is a major risk factor for impaired NAD+ metabolism, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other metabolic disorders. Early detection of NAD+ deficiency symptoms and risk factors is vital for effective intervention and management.
Cardiovascular diseases and neurodegenerative disorders are linked to low NAD+ levels. The decline in NAD+ can lead to oxidative damage and DNA damage, contributing to the development and progression of these conditions. Addressing NAD+ deficiency is essential for preventing and managing several diseases, including heart failure and metabolic conditions.
Recognising major risk factors and symptoms of severe NAD+ deficiency aids in early diagnosis and treatment, reducing health complications and leading to a significant difference in outcomes.
NAD+ Research and Future Directions
NAD+ has emerged as a critical molecule in aging processes, garnering significant scientific interest. Research focuses on understanding the long-term effects and mechanisms of NAD+ boosters on aging. There is growing interest in using these boosters as dietary supplements due to their potential anti-aging effects.
Despite promising findings, few studies have conclusively established the benefits of NAD+ boosters. Further research is needed to understand the long-term effects and mechanisms through which NAD+ influences aging and related diseases. Future breakthroughs could reveal new therapeutic strategies for age-related diseases by harnessing NAD+ metabolism.
Understanding NAD+’s role in cellular processes like signal transduction and DNA repair is crucial for developing effective interventions. Researchers are exploring metabolic pathways and reactions involving NAD+ to uncover its full potential in promoting health and longevity.
As we learn more about NAD+, the potential for innovative treatments and preventive measures grows. The future of NAD+ research holds promise for enhancing our understanding of aging research and developing strategies to improve health span and life span.
Summary
In conclusion, NAD+ is an essential molecule that plays a critical role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and overall cellular health. Understanding the age-dependent decline of NAD+ levels and the factors that influence this decline is crucial for addressing the associated health implications.
By monitoring NAD+ levels and adopting strategies to boost NAD+, we can mitigate the effects of aging and improve overall health. The latest research and future directions in NAD+ studies offer hope for new therapeutic approaches to age-related diseases and enhanced longevity.
Taking proactive steps to maintain healthy NAD+ levels can lead to a healthier, more vibrant life. Stay informed, take control of your health, and embrace the potential of NAD+ to support your well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
At what age do NAD+ levels start to decline?
NAD+ levels begin to decline around age 30, with notable decreases occurring from young adulthood to middle age. This reduction can impact various physiological processes.
How can I test my NAD+ levels at home?
You can test your NAD+ levels at home using a specialised NAD+ test kit that includes a blood-spot assay card to collect samples. These samples are then analysed through advanced methods like high-resolution liquid chromatography.
What are some common symptoms of NAD+ deficiency?
Common symptoms of NAD+ deficiency include fatigue, cognitive decline, poor sleep quality, mental fog, and skin changes like increased dryness and wrinkles. Addressing these symptoms early could be beneficial for your overall health.
What lifestyle changes can help boost NAD+ levels?
To boost NAD+ levels, incorporate raw foods rich in B vitamins, consume fermented foods, practice intermittent fasting, and spend time in saunas while limiting sun exposure. These lifestyle changes can significantly enhance your cellular health and energy levels.
Why is NAD+ important for overall health?
NAD+ is vital for energy metabolism, DNA repair, and overall cellular health, playing a key role in mitigating aging and age-related diseases. Keeping NAD+ levels balanced is essential for optimal physiological function.
NMN vs. NAD⁺ Brain — What’s the difference?
Our NAD+ Brain formula doesn’t contain NAD+ directly — and that’s intentional. Instead, we use NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) to boost your body’s own production of NAD⁺. Once NAD⁺ levels are elevated, the NAD+ Brain formula helps keep that NAD+ active and available where it’s needed most — especially in the brain.
Think of it this way:
NMN builds the NAD+. NAD+ Brain helps you hold onto it.
NAD+ Brain is our proprietary blend crafted to enhance cognitive performance.
Our NMN supplement works to directly raise your NAD+ levels, powering better energy, focus, and longevity.
Researched and reviewed by Dr Elena Seranova, Ph.D.
Dr Seranova holds a master's degree in Translational Neuroscience from the University of Sheffield, UK, and a Ph.D in Stem Cell Biology and Autophagy from the University of Birmingham, UK. She is a published author in multiple peer-reviewed journals, including Cell Reports and Developmental Cell.
LEARN MORE!






Leave a comment